Learning how to mine Ethereum can be rewarding for those looking to participate in cryptocurrency.
Ethereum mining is crucial in securing the network and processing transactions. As a reward, miners can earn Ether (ETH).
One of the most well-known cryptocurrencies, Ethereum, runs on a solid blockchain network driven by mining.
Mining keeps Ethereum’s decentralized system running. It performs complicated math to ensure that transactions are confirmed and added to the blockchain.
Ethereum offers many great opportunities for people who want to make money by mining, but it also has some problems that need to be solved.
One of the advantages of mining Ethereum is the opportunity to earn Ether (ETH), contribute to the network’s security, and gain a deeper understanding of blockchain technology.
However, it’s essential to be aware of the potential risks, such as high energy costs, market volatility, and the upcoming transition to Ethereum 2.0 and its Proof-of-Stake (PoS) model, which can offset the potential benefits.
This step-by-step guide will teach you everything you need to know to begin mining Ethereum.
It includes essential tools, methods, and information that will help you make intelligent choices and get the most out of your mining experience.
Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding Ethereum Mining: How to Mine Ethereum

How Ethereum Mining Works
At the heart of Ethereum mining lies the concept of Proof-of-Work (PoW), a consensus mechanism designed to secure the network and validate transactions.
In PoW, miners compete to solve complex mathematical puzzles, using significant computational power to find a unique solution, or “hash,” for a new block.
Once a miner successfully solves the puzzle, the new block is validated and added to the Ethereum blockchain, and the miner is rewarded with Ether (ETH).
This mining process not only ensures that transactions are verified and immutable but also prevents attacks on the network, as the immense energy and computational costs make fraudulent activity impractical.
The mining process involves:
- Gathering unconfirmed transactions from the network.
- Organizing them into a block.
- Solving a cryptographic problem that ties the new block to the previous one.
Each block contains a hash of the previous block, forming a continuous, secure chain.
The first miner to successfully solve the cryptographic problem broadcasts the block to the network, and other nodes verify its validity.
Once confirmed, the block is added to the chain, and the process repeats with a new block.
Ethereum 2.0 and Proof-of-Stake (PoS) Transition
With the introduction of Ethereum 2.0, the network is transitioning from the energy-intensive Proof-of-Work model to a more sustainable and efficient Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism.
Unlike PoW, PoS eliminates the need for massive computational resources.
Instead of miners competing to solve puzzles, validators are chosen to create new blocks based on the amount of Ether they hold and are willing to “stake” as collateral.
Validators are rewarded for their participation in maintaining the network, but they also risk losing their staked Ether if they attempt to act maliciously.
This transition to Ethereum 2.0 will have a significant impact on mining.
Once Ethereum fully shifts to PoS, traditional mining using GPUs or ASICs will no longer be viable, as the network will no longer require miners to solve cryptographic puzzles.
Instead, network participants will need to stake Ether to participate in the validation process.
As a result, current Ethereum miners will either need to repurpose their hardware for mining other cryptocurrencies or transition to becoming validators in the new PoS system.
This shift aims to reduce energy consumption, improve scalability, and increase security in the long run. However, it also marks the end of Ethereum’s traditional mining model.
Essential Tools for Ethereum Mining
Mining Hardware
When mining hardware, you have two main options: GPUs (Graphics Processing Units) and ASICs (Application-Specific Integrated Circuits).
GPUs are versatile and can be used for various tasks beyond mining, making them a popular choice for many miners.
They are also more accessible and provide flexibility in mining different cryptocurrencies.
On the other hand, ASICs are designed specifically for mining and offer greater efficiency and higher hash rates, which means faster mining results.
However, ASICs can be more expensive and lack the flexibility of GPUs, as they are usually designed for specific algorithms like Ethereum’s Ethash.
For recommended hardware options, high-performance GPUs such as the Nvidia GeForce RTX 3060 Ti or AMD Radeon RX 6800 are top picks for Ethereum mining.
These GPUs offer a good balance of power efficiency and hashing performance.
If you prefer ASICs, models like the Innosilicon A10 Pro+ or Bitmain Antminer E9 are excellent choices, delivering higher mining efficiency but at a steeper price.
New Antminer S19 Bitmain Bitcoin Miner 90T 3105W Include PSU Asic Mining SHA-256 Hardware by OEMGMINER (90T)
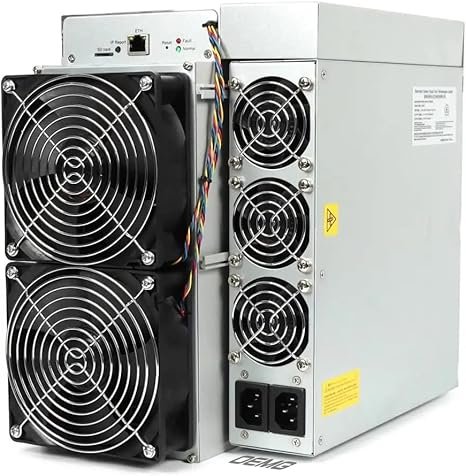

| Model Name | goldshell |
| Brand | OEMGMINER |
| Compatible Devices | Personal Computer |
| Connector Type | ATX |
| Output Wattage | 2829 Watts |
| Form Factor | ATX |
| Wattage | 2829 watts |
| Cooling Method | Air |
| Power Supply Design | External |
| Minimum Input Voltage | 1E+2 Volts (AC) |
Mining Software
Choosing the right mining software is equally important for successful Ethereum mining.
Popular mining software options include Claymore, PhoenixMiner, and Ethminer, all of which are well-known for their reliability and compatibility with Ethereum’s mining algorithm.
Claymore offers dual mining capabilities, allowing miners to mine two cryptocurrencies simultaneously, while PhoenixMiner is favored for its speed and efficiency.
Ethminer is an open-source option with broad community support, making it easy to set up and customize.
When choosing the right software, consider factors like ease of use, compatibility with your hardware, and the ability to tweak settings for optimization.
For beginners, software with a user-friendly interface like NiceHash may be ideal, as it simplifies the mining process and automatically switches to the most profitable coin.
For more advanced miners, software like PhoenixMiner, which allows manual optimization of settings such as overclocking and undervolting, may be more appropriate for maximizing mining efficiency.
Operating Systems for Mining
The two most common operating systems for Ethereum mining are Windows and Linux.
Windows is a popular choice among beginners because of its familiar interface and wide compatibility with mining software.
Many mining programs are designed to run smoothly on Windows, making setting up and managing your mining rig easier.
However, Windows can be more resource-intensive, requiring regular updates and more system memory to run efficiently.
On the other hand, Linux offers better mining efficiency for advanced users who are comfortable with its command-line interface.
It consumes fewer system resources, allows for better control over hardware settings, and is generally more stable for long-term mining operations.
Linux distributions like Ubuntu or HiveOS are excellent choices for users who prioritize efficiency.
They provide streamlined mining environments with fewer interruptions and greater control over performance settings.
Ultimately, your choice between Windows and Linux depends on your experience level and preference for ease of use versus mining efficiency.
Setting Up Your Mining Rig

Building a Mining Rig
The first step in building a mining rig is gathering the essential components.
For Ethereum mining, you’ll need the following key hardware: GPUs (the most critical component for hashing power), a motherboard with multiple PCIe slots for connecting multiple GPUs, a power supply unit (PSU) capable of providing enough wattage for all components, RAM (usually 8GB is sufficient), a CPU (basic models work fine as mining doesn’t rely heavily on CPU power), storage (a small SSD is sufficient for mining software and operating systems), and a rig frame to hold everything in place.
You’ll also need cooling fans to manage heat from the GPUs and other components.
Once you’ve gathered all the components, follow this step-by-step assembly guide:
Install the CPU onto the motherboard and secure it with the cooling fan.
Insert the RAM into the appropriate slot on the motherboard.
Mount the motherboard onto the rig frame and secure it.
Attach the power supply unit (PSU) to the frame and connect it to the motherboard and GPUs.
Install the GPUs into the PCIe slots, ensuring they are secured in place. If needed, use risers to connect the GPUs to the motherboard.
Connect all the power cables from the PSU to the GPUs and other components.
Attach the SSD and connect it to the motherboard.
Finally, connect the cooling fans and ensure all components are properly wired and secured.
Once the assembly is complete, your rig is ready for configuration.
Configuring Your Mining Rig
Configuring your mining rig involves adjusting the BIOS settings for optimal performance and ensuring your software is set up correctly.
To start, you’ll need to access the BIOS settings on your motherboard. One crucial adjustment is enabling Above 4G Decoding, which allows your motherboard to recognize all GPUs in the system.
Additionally, change the PCIe Link Speed to Gen2 for stability, and disable any unnecessary features like C-States and Power Saving Mode to ensure maximum efficiency.
If you’re using risers, make sure they are recognized by the system, and update your motherboard’s BIOS to the latest version to avoid compatibility issues.
Next comes software installation and configuration. First, install your preferred operating system, such as Windows or a Linux-based mining OS like HiveOS.
After the OS is installed, download and install the mining software you’ve chosen (e.g., PhoenixMiner, Claymore, or Ethminer).
You’ll need to configure the mining software by entering your wallet address, selecting the mining pool, and optimizing the settings for performance.
This includes adjusting the hash rate, power limits, and overclocking settings for your GPUs to maximize efficiency and profitability.
Regularly monitor your rig’s performance to ensure it’s running optimally, and make any necessary tweaks to improve stability and output.
Mining Pools: What They Are and Why They Matter
Introduction to Mining Pools
A mining pool is a collaborative group of miners who pool their computing resources to increase their chances of successfully mining a block.
Individual miners may struggle to find blocks in Ethereum mining due to the high network difficulty and increasing competition.
By joining a mining pool, miners combine their hash power, and if the pool successfully mines a block, the rewards are shared among all members based on their contribution.
The advantages of pool mining are significant, particularly for those with limited hardware or computational power.
Pool mining provides more consistent payouts, reducing the volatility and long waiting periods that solo miners may experience.
Additionally, pooling resources allows miners to compete against larger, more powerful operations, ensuring they still earn a portion of the rewards even if their individual mining setup is not powerful enough to mine on its own.
Choosing the Right Mining Pool
When choosing the right mining pool, several factors need to be considered.
First, look at the pool’s fee structure—most mining pools charge a small fee, typically between 1% and 3%, of the rewards, so it’s important to find a pool with a reasonable fee that doesn’t cut too much into your profits.
Next, consider the pool’s hash rate—larger pools with higher hash rates are more likely to find blocks more frequently, leading to more consistent payouts.
However, these larger pools also distribute rewards among more miners, which can result in smaller individual payouts.
Additionally, check the pool’s minimum payout threshold—you want a pool with a threshold that aligns with how often you prefer to receive payouts.
A comparison of popular mining pools reveals some top choices for Ethereum mining.
Ethermine is one of the largest pools, known for its low fees and stable payouts. F2Pool is another reliable option with a user-friendly interface and a global presence.
SparkPool is also popular, offering competitive fees and high-performance servers. Each pool has its own strengths, so it’s important to consider your specific needs when choosing.
Joining a Mining Pool
Once you’ve selected a pool, joining it is straightforward. First, you’ll need to register an account on the pool’s website.
During registration, you’ll typically provide your wallet address where your mining rewards will be sent, and you may need to set up a username and worker ID for tracking your mining performance.
After registering, the next step is configuring your mining software for pool mining. To do this, input the pool’s server address and your wallet credentials into your mining software’s configuration settings.
This will direct your mining power to the pool. Most mining software also allows you to monitor your performance and earnings in real-time, making it easy to track your contribution and rewards from the pool.
Regularly check your setup to ensure you’re connected to the pool and mining efficiently.
Mining Strategies and Best Practices
Optimizing Mining Performance
To maximize your Ethereum mining performance, it’s essential to focus on overclocking and undervolting.
Overclocking involves increasing the clock speed of your GPU beyond its default settings to enhance its processing power, which can lead to higher hash rates. However, pushing your hardware too far can result in instability, so it’s important to find the right balance.
Undervolting, on the other hand, reduces the voltage supplied to the GPU while maintaining performance. This reduces power consumption and heat generation, making your rig more efficient and extending the lifespan of your components.
Effective cooling solutions and ventilation are critical for maintaining optimal mining performance. High-powered GPUs generate substantial heat, which can degrade performance or damage hardware if not properly managed.
Consider using high-performance cooling fans, liquid cooling systems, or external ventilation to dissipate heat effectively. Proper airflow within your mining rig is essential, so position your rig in a well-ventilated area, and clean your components regularly to prevent dust buildup.
Calculating Profitability
Understanding hash rate and difficulty is crucial for determining the profitability of Ethereum mining.
Hash rate refers to the speed at which your mining rig can solve the cryptographic puzzles necessary to mine Ethereum. A higher hash rate generally translates to better mining performance.
Difficulty measures how hard it is to mine a new block on the Ethereum network, which fluctuates based on the total computational power of the network.
As more miners join the network, the difficulty increases, potentially reducing profitability.
To accurately assess your earnings, use tools for profitability calculation such as WhatToMine or CryptoCompare.
These platforms allow you to input key metrics like your rig’s hash rate, power consumption, and electricity costs to calculate your potential profits.
Regularly checking profitability helps ensure that your mining setup remains viable, especially as network conditions and energy costs change.
Avoiding Common Pitfalls
When mining Ethereum, you may encounter technical challenges, so it’s important to understand troubleshooting common issues.
Some frequent problems include GPU crashes due to unstable overclocking settings, driver conflicts, or incorrect BIOS configurations.
Monitoring your mining rig’s performance and temperatures can help you detect problems early.
If your rig frequently crashes or underperforms, consider adjusting your overclocking settings, updating your drivers, or reverting to more stable BIOS settings.
In addition, taking security measures to protect your rig is essential. Mining rigs are often targets for cyberattacks, especially malware that hijacks computational power or steals cryptocurrency.
To mitigate risks, use strong passwords, enable two-factor authentication, and ensure that your mining software and operating system are always updated to patch security vulnerabilities.
Furthermore, installing a reliable firewall and antivirus software can help safeguard your rig against potential threats.
Advanced Mining Techniques
Cloud Mining
Cloud mining is an alternative method of mining Ethereum where individuals rent computational power from large data centers rather than operating their own hardware.
This service allows users to mine cryptocurrencies without purchasing, maintaining, or configuring any physical mining equipment.
Instead, users sign contracts with cloud mining providers who handle the technical aspects of mining and pay users a portion of the rewards based on their contract terms.
There are several pros and cons of cloud mining to consider. The major advantage is its simplicity—cloud mining eliminates the need for expensive hardware, maintenance, and high electricity bills.
It’s a more accessible option for beginners who want to participate in Ethereum mining without the technical complexity of setting up a rig.
Additionally, cloud mining contracts offer flexibility, allowing users to choose different mining durations and computational power.
However, cloud mining also has notable downsides. One of the biggest risks is profitability—many cloud mining services charge high fees, and the returns may not always cover the upfront costs.
In some cases, cloud mining contracts may become unprofitable if Ethereum’s network difficulty increases or market conditions change.
Furthermore, there’s a risk of scams in the cloud mining industry, with some companies offering fraudulent services or disappearing with users’ funds.
Therefore, careful research is essential before committing to any cloud mining provider.
Solo Mining vs. Pool Mining
When deciding between solo mining and pool mining, it’s important to understand the key differences.
Solo mining involves mining independently, meaning that the miner is solely responsible for finding and validating blocks.
While the rewards are higher for each block successfully mined, solo mining has become increasingly challenging due to the rise in Ethereum’s mining difficulty and competition.
With solo mining, long periods may pass without any rewards, as mining a block is largely dependent on the miner’s hash rate and luck.
In contrast, pool mining allows miners to combine their hash rate with others in a mining pool, increasing the chances of successfully mining blocks more frequently.
In pool mining, the rewards are shared among all participants based on their contribution to the pool’s overall hash rate.
Although individual payouts are smaller in pool mining, they are more consistent and reliable, making pool mining a popular choice for those without high-end hardware.
The decision on when to consider solo mining largely depends on the scale of your mining operation and your hardware capabilities.
Solo mining may be suitable for individuals or businesses with significant computational power, such as those with access to powerful ASIC miners or large mining farms.
Solo mining can offer potentially higher rewards if you can generate a high hash rate and are willing to take on the risk of irregular payouts.
However, pool mining is safer and more stable for most miners, particularly those with less powerful equipment.
Regulatory and Legal Considerations
Understanding Legal Implications
Ethereum mining is subject to various regulations around mining in different regions, and these laws can vary significantly from one country to another.
In some countries, cryptocurrency mining is fully legal and even encouraged, while in others it is heavily restricted or banned due to concerns over energy consumption, environmental impact, or regulatory uncertainty.
For example, countries like the U.S. and Canada allow cryptocurrency mining but may impose specific regulations around energy usage, licensing, and data center operations.
In contrast, nations such as China have introduced strict bans on crypto mining due to concerns over energy waste and capital flight.
Therefore, miners must ensure they are aware of local laws before beginning their operations.
In addition to regional regulations, there are also important tax implications for miners.
Many jurisdictions often treat Ethereum mining as taxable income, and miners must report their earnings to the relevant tax authorities.
Depending on the country, miners may need to pay income tax on the rewards they receive, capital gains tax when they sell or exchange their mined Ethereum, and in some cases, VAT or other transaction taxes.
Failing to report mining earnings properly can result in fines or legal penalties, so it’s essential to consult with a tax professional or accountant familiar with cryptocurrency laws.
Best Practices for Compliance
Adopting best practices for compliance, starting with keeping records, is crucial to ensuring that mining operations comply with regulations.
Proper record-keeping is essential for both tax reporting and regulatory purposes.
Miners should maintain detailed logs of all mining activities, including the date, time, and value of Ethereum rewards received, electricity costs, and any hardware or software purchases.
These records are necessary to calculate profitability, track expenses, and file accurate tax returns.
Additionally, miners must stay informed about regulations to stay up-to-date with evolving laws.
Cryptocurrency laws are constantly changing, and miners should monitor new developments in their country or region.
Regularly consulting legal experts, joining cryptocurrency mining forums, or subscribing to industry news outlets can help ensure that miners remain compliant with the latest regulations.
Being proactive about legal changes can help miners avoid potential legal pitfalls and ensure their operations remain legitimate.
Future of Ethereum Mining
Impact of Ethereum 2.0 on Mining
The transition to Ethereum 2.0 represents a monumental shift for the Ethereum network and its mining ecosystem.
With Ethereum 2.0, the network is moving from the energy-intensive Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus mechanism to a more efficient Proof-of-Stake (PoS) model.
In the PoW system, miners solve complex mathematical problems to validate transactions and secure the network, earning rewards for their efforts. However, PoS eliminates the need for this process.
Instead of miners, validators are chosen to create new blocks based on the amount of Ethereum they hold and stake in the network.
This transition to Proof-of-Stake has major implications for Ethereum mining. Once Ethereum fully switches to PoS, traditional mining will no longer be required.
As a result, miners will no longer be able to profit from mining Ether as they did under PoW.
This change is expected to greatly reduce the energy consumption associated with Ethereum, but it also means that those who have invested in mining hardware, such as GPUs and ASICs, will need to adapt.
Some may choose to sell or repurpose their equipment for mining other cryptocurrencies that still use PoW, while others may transition to staking Ethereum to earn rewards.
Emerging Trends in Mining Technology
Despite the changes brought by Ethereum 2.0, there are still emerging trends in mining technology that impact the broader cryptocurrency mining landscape.
One major trend is the development of more energy-efficient mining hardware.
As environmental concerns grow, miners and manufacturers are seeking ways to reduce electricity consumption and improve the profitability of mining operations.
Innovations like liquid cooling systems and specialized hardware designed for specific cryptocurrencies are becoming more popular.
Another significant innovation is the rise of decentralized mining pools. Traditional mining pools are often centralized, creating potential vulnerabilities and trust issues.
Decentralized mining pools offer a solution by spreading the validation process across multiple nodes, ensuring greater security and transparency.
This development aligns with the broader ethos of decentralization that underpins the cryptocurrency space.
To stay ahead in the mining industry, miners must be proactive in adopting new technologies and adjusting their strategies to remain competitive.
Keeping an eye on hardware developments, participating in forward-thinking mining communities, and staying informed about the latest industry trends are essential steps.
Additionally, exploring opportunities in other PoW cryptocurrencies or transitioning to PoS through staking can help miners maintain profitability in a rapidly changing environment.
Conclusion: How to Mine Ethereum
In this comprehensive guide on how to mine Ethereum, we’ve explored the essential tools, pools, and strategies necessary for successful mining operations.
From understanding the fundamentals of Proof-of-Work and Ethereum 2.0’s transition to Proof-of-Stake, to selecting the right hardware and software, setting up your mining rig, and optimizing your mining performance, we’ve covered the critical aspects needed to navigate the world of Ethereum mining.
Additionally, we’ve delved into the nuances of mining pools, advanced techniques such as cloud mining and solo mining, and crucial regulatory and legal considerations.
As Ethereum continues to evolve, staying informed about the latest trends and technologies will be key to maintaining a competitive edge.
Whether you’re just starting out or looking to refine your existing setup, applying these strategies and practices will help you maximize your mining efficiency and profitability.
If you found this guide helpful, please share it with others who might benefit from it, and subscribe to our email newsletter for more insights and updates.
If you have any questions or need further clarification, feel free to comment below—I’d love to hear from you!
FAQs: How to Mine Ethereum
What is the best hardware for Ethereum mining?
The best hardware for Ethereum mining in 2024 typically includes high-performance GPUs such as the NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3090 or AMD Radeon RX 6900 XT. These GPUs offer excellent hash rates and energy efficiency. For specialized mining, ASIC miners like the Antminer E9 are also viable, but their availability and cost can vary.
How much can I earn from mining Ethereum?
Earnings from mining Ethereum depend on factors such as hash rate, electricity costs, and current Ethereum prices. As of 2024, profitability calculators can help estimate potential earnings based on these variables. Generally, higher hash rates and lower electricity costs lead to better profitability.
Is it worth investing in mining Ethereum in 2024?
Investing in Ethereum mining in 2024 depends on several factors, including Ethereum’s transition to Proof-of-Stake, hardware costs, and electricity expenses. With Ethereum 2.0 reducing reliance on mining, it might be more profitable to invest in staking or alternative cryptocurrencies.
How do I troubleshoot issues with my mining rig?
To troubleshoot mining rig issues:
- Start by checking hardware connections and ensuring components are functioning correctly.
- Verify that the mining software is updated and configured properly.
- For persistent problems, review error logs, check for overheating issues, and consult online forums or technical support for guidance.
What are the tax implications of mining Ethereum?
Mining Ethereum is generally considered taxable income, and you may need to report earnings based on the fair market value of the Ethereum at the time of mining. Additionally, you might be subject to capital gains tax when selling or trading mined Ethereum. It’s essential to keep detailed records and consult a tax professional for accurate reporting.








Your writing is a true testament to your expertise and dedication to your craft. I’m continually impressed by the depth of your knowledge and the clarity of your explanations. Keep up the phenomenal work!